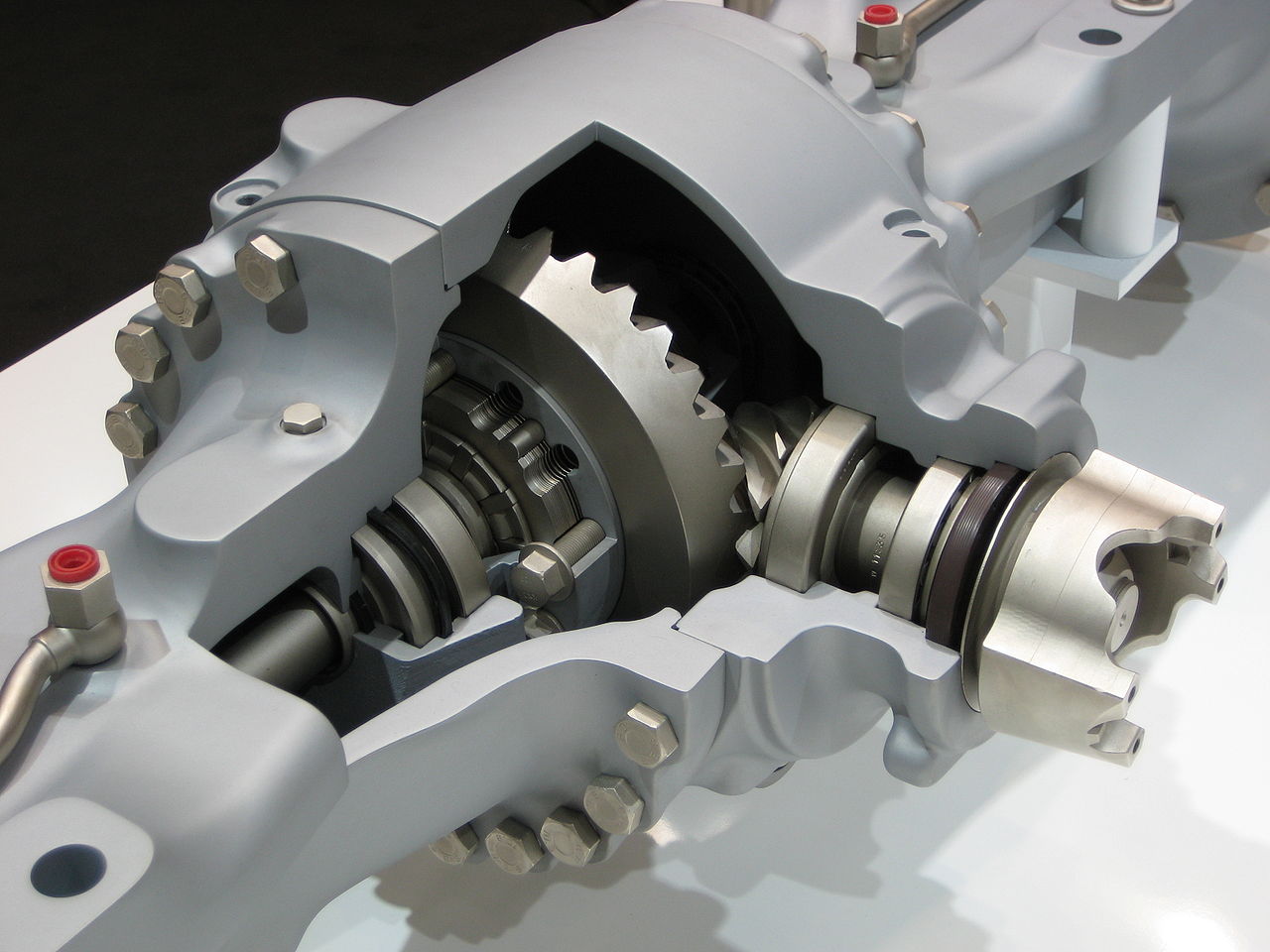
A limited-slip differential is a type of automotive differential gear arrangement that allows for some difference in angular velocity of the output shafts, but imposes a mechanical limit on the disparity.
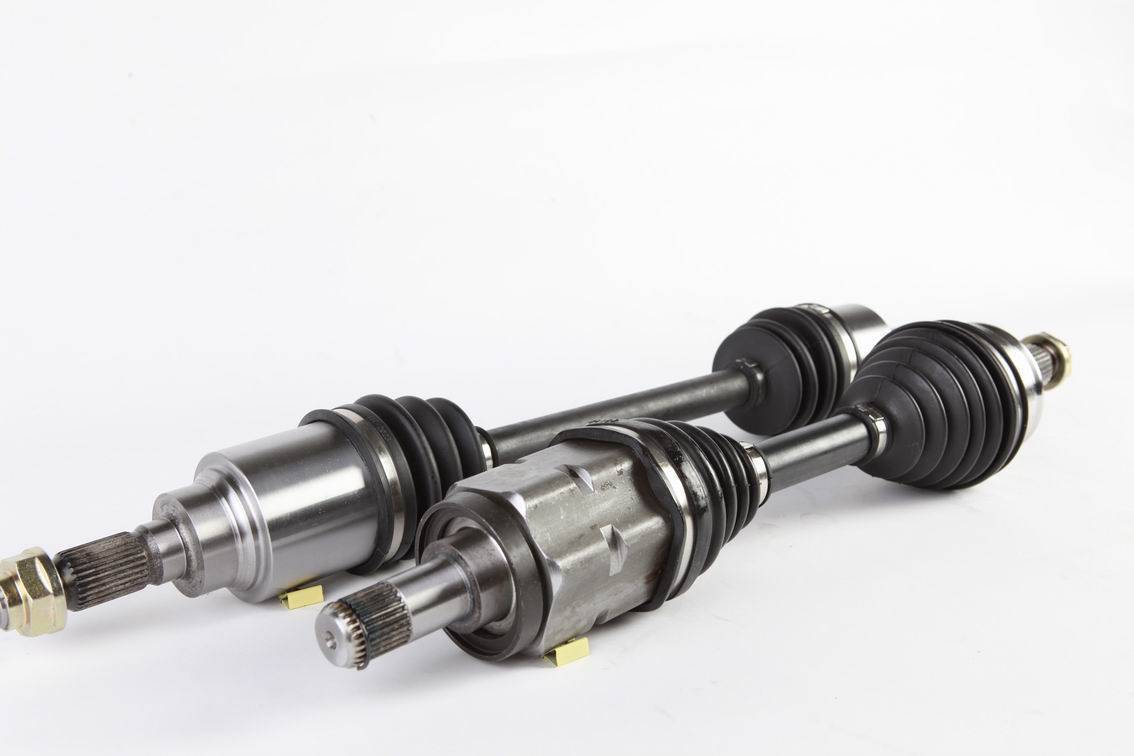
Constant-velocity joints (AKA homokinetic or CV joints) allow a drive shaft to transmit power through a variable angle, at constant rotational speed, without an appreciable increase in friction or play.
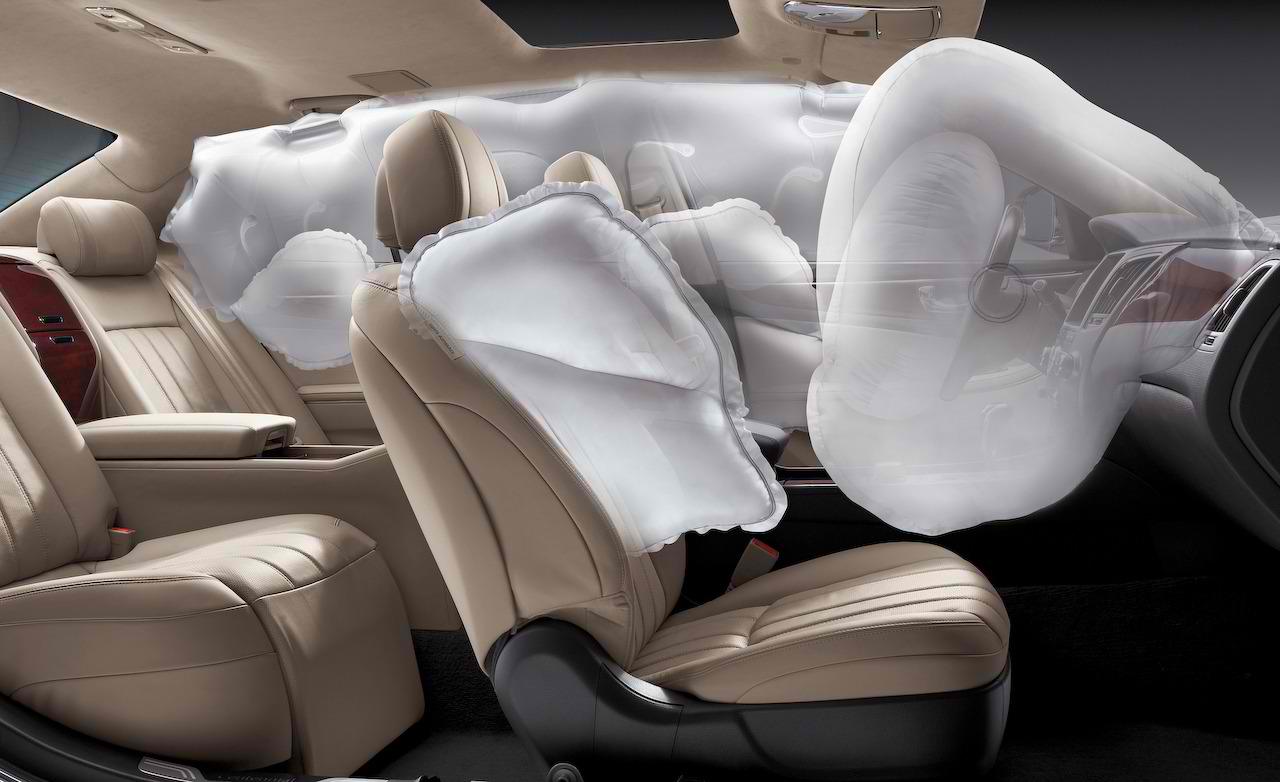
An airbag is a type of vehicle safety device and is an occupant restraint system.
Curb weight (US English) or kerb weight (UK English) is the total weight of a vehicle with standard equipment
The static compression ratio of an internal-combustion engine or external combustion engine is a value that represents the ratio of the volume of its combustion chamberfrom its largest capacity to its smallest capacity.
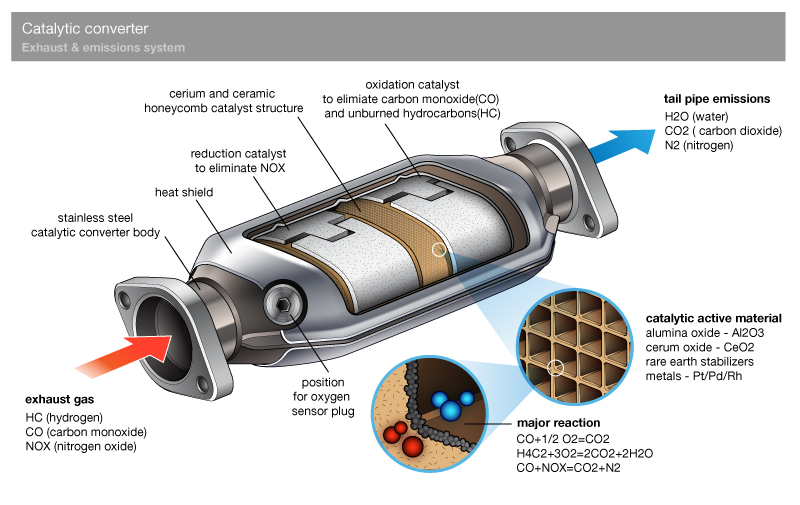
A catalytic converter is an emissions control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas to less toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction (an oxidation and a reduction reaction).
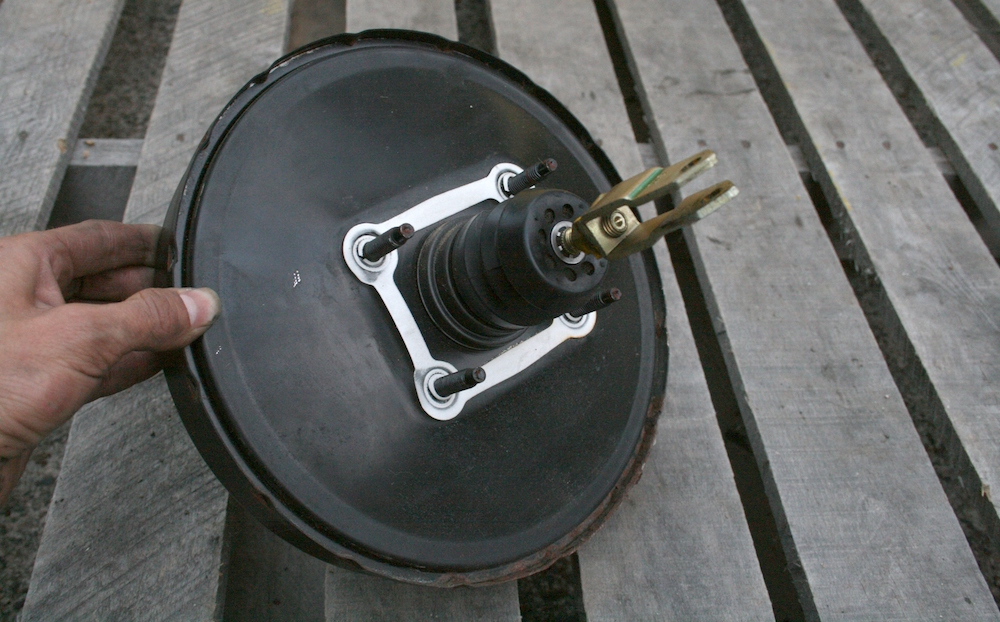
A vacuum servo is a component used on motor vehicles in their braking system, to provide assistance to the driver by decreasing the braking effort. In the US it is commonly called a brake booster.
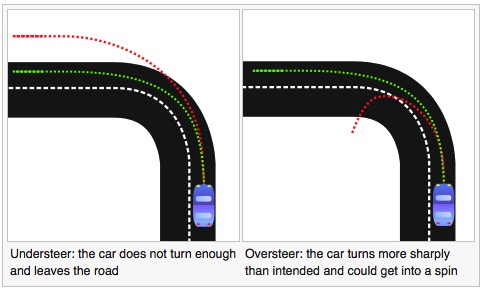
Understeer and oversteer are vehicle dynamics terms used to describe the sensitivity of a vehicle to steering.
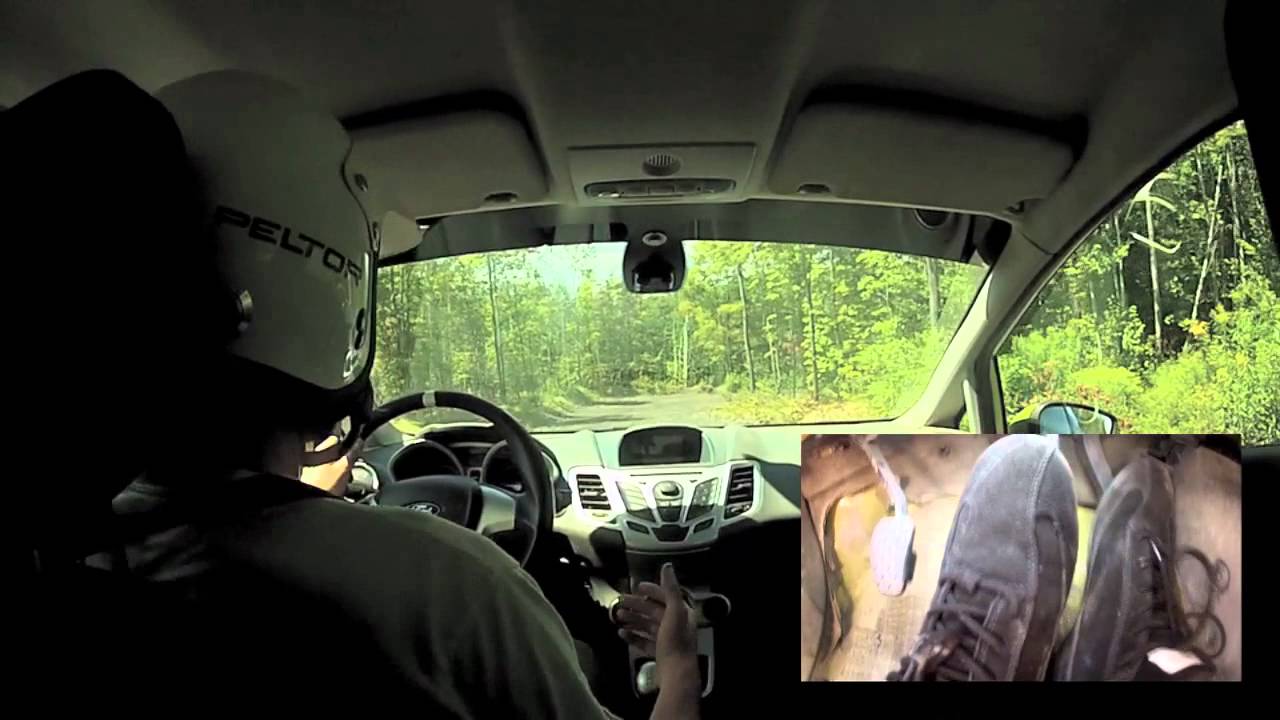
Left-foot braking is the technique of using the left foot to operate the brake pedal in an automobile, leaving the right foot dedicated to the throttle pedal.
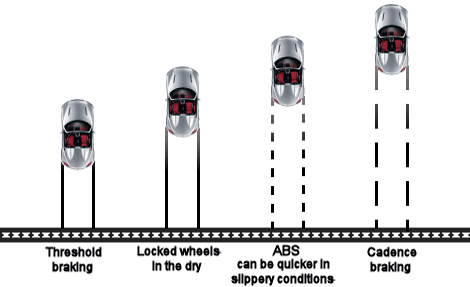
Cadence braking or stutter braking is an advanced driving technique that involves pumping the brake pedal and is used to allow a car to both steer and brake on a slippery surface.