
Tue, Oct 25, 2016 9:57 PM
Image: computra.startlogic.com
Bike geometry is the collection of key measurements (lengths and angles) that define a particular bike configuration. Primary among these are wheelbase, steering axis angle, fork offset, and trail.
These parameters have a major influence on how a bike handles.
Wheelbase
Wheelbase is the horizontal distance between the centers (or the ground contact points) of the front and rear wheels. Wheelbase is a function of rear frame length, steering axis angle, and fork offset. It is similar to the term wheelbase used for automobiles and trains.
Wheelbase has a major influence on the longitudinal stability of a bike, along with the height of the center of mass of the combined bike and rider. Short bikes are much more suitable for performing wheelies and stoppies.
Steering axis angle
The steering axis angle, also called caster angle or head angle, is the angle that the steering axis makes with the horizontal or vertical, depending on convention. The steering axis is the axis about which the steering mechanism (fork, handlebars, front wheel, etc.) pivots. The steering axis angle usually matches the angle of the head tube.
bike Head Angle
In bikes, the steering axis angle is called the head angle and is measured from the horizontal; a 90° head angle would be vertical. For example, Lemond offers:
- a 2007 Filmore, designed for the track, with a head angle that varies from 72.5° to 74° depending on frame size
- a 2006 Tete de Course, designed for road racing, with a head angle that varies from 71.25° to 74°, depending on frame size.
Due to front fork suspension, modern Mountain Bikes as opposed to Road Bikes, tend to have slacker head tube angles, generally around 70° although they can be as low as 68° (depending on frame size).
At least one manufacturer, Cane Creek, offers an after-market threadless headset that enables changing the steering axis angle. When all else remains the same, this alters the trail of the bike.
Motorcycle Rake Angle
In motorcycles, the steering axis angle is called the rake angle or just rake and is measured from the vertical. A 0° rake would be vertical. For example, Moto Guzzi offers:
- a 2007 Breva V 1100 with a rake of 25°30’ (25.5 degrees)
- a 2007 Nevada Classic 750 with a rake of 27.5°
Fork offset
The fork offset is the perpendicular distance from the steering axis to the center of the front wheel.
In bikes, fork offset is also called fork rake. Road racing bike forks have an offset of 40–50 mm (1.6–2.0 in).
The offset may be implemented by curving the forks, adding a perpendicular tab at their lower ends, offseting the fork blade sockets of the fork crown ahead of the steerer, or by mounting the forks into the crown at an angle to the steer tube. The development of forks with curves is attributed to George Singer.
In motorcycles with telescopic fork tubes, fork offset can be implemented by either an offset in the triple tree, adding a triple tree rake (usually measured in degrees from 0) to the fork tubes as they mount into the triple tree, or a combination of the two. Other, less-common motorcycle forks, such as trailing link or leading link forks, can implement offset by the length of link arms.
Fork length
The length of a fork is measured parallel to the steer tube from the lower fork crown bearing to the axle center.
Trail
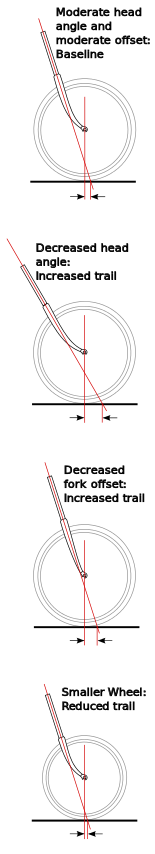 A diagram showing the effect of decreasing the head tube angle or the fork offset on the trail.
A diagram showing the effect of decreasing the head tube angle or the fork offset on the trail.
Trail, or caster, is the horizontal distance from where the front wheel touches the ground to where the steering axis intersects the ground. The measurement is considered positive if the front wheel ground contact point is behind (towards the rear of the bike) the steering axis intersection with the ground. Most bikes have positive trail, though a few, such as the two-mass-skate bike and the Python Lowracer have negative trail.
Trail is often cited as an important determinant of bike handling characteristics, and is sometimes listed in bike manufacturers' geometry data, although Wilson and Papodopoulos argue that mechanical trail may be a more important and informative variable, although they both describe very nearly the same thing.
Trail is a function of steering axis angle, fork offset, and wheel size. Their relationship can be described by this formula:
{\displaystyle {\text{Trail}}_{\text{ bike}}={\frac {R_{w}\cos(A_{h})-O_{f}}{\sin(A_{h})}}}
where {\displaystyle R_{w}}



Motorcyclists tend to speak of trail in relation to rake angle. The larger the rake angle the larger the trail. Note that, on a bike, as rake angle increases, head angle decreases.
Trail can vary as the bike leans or steers. In the case of traditional geometry, trail decreases (and wheelbase increases if measuring distance between ground contact points and not hubs) as the bike leans and steers in the direction of the lean. Trail can also vary as the suspension activates, in response to braking for example. As telescopic forks compress due to load transfer during braking, the trail and the wheelbase both decrease. At least one motorcycle, the MotoCzysz C1, has a fork with adjustable trail, from 89 mm to 101 mm.
Mechanical trail
Mechanical trail is the perpendicular distance between the steering axis and the point of contact between the front wheel and the ground. It may also be referred to as normal trail. In each case, its value is equal to the numerator in the expression for trail.
{\displaystyle {\text{MechanicalTrail}}_{\text{motorcycle}}=R_{w}\sin(A_{r})-O_{f}}
Although the scientific understanding of steering remains incomplete, mechanical trail is certainly one of the most important variables in determining the handling characteristics of a bike. Several reasons make a trail of zero seem ideal:
- the influence of the position of the center of pressure of wind forces coming from the side is eliminated
- the wheel flop effect (see below) is eliminated
- in theory stability of the vehicle increases (as the computed deviation from the ideal path during steering action is reduced).
Skilled and alert riders may have more path control if the mechanical trail is lower while a higher trail is known to make a bike easier to ride "no hands" and thus more subjectively stable.
Wheel flop
Wheel flop refers to steering behavior in which a bike or motorcycle tends to turn more than expected due to the front wheel "flopping" over when the handlebars are rotated. Wheel flop is caused by the lowering of the front end of a bike or motorcycle as the handlebars are rotated away from the "straight ahead" position. This lowering phenomenon occurs according to the following equation:
{\displaystyle f=b\sin \vartheta \cos \vartheta }
where:
{\displaystyle f}
{\displaystyle b}
{\displaystyle \vartheta }
Because wheel flop involves the lowering of the front end of a bike or motorcycle, the force due to gravity will tend to cause handlebar rotation to continue with increasing rotational velocity and without additional rider input on the handlebars. Once the handlebars are turned, the rider needs to apply torque to the handlebars to bring them back to the straight ahead position and bring the front end of the bike or motorcycle back up to the original height. The rotational inertia of the front wheel will lessen the severity of the wheel flop effect because it results in opposing torque being required to initiate or accelerate changing the direction of the front wheel.
According to the equation listed above, increasing the trail and/or decreasing the head angle will increase the wheel flop factor on a bike or motorcycle, which will increase the torque required to bring the handlebars back to the straight ahead position and increase the vehicle's tendency to veer suddenly off the line of a curve. Also, increasing the weight borne by the front wheel of the vehicle, either by increasing the mass of the vehicle, rider and cargo or by changing the weight ratio to shift the center of mass forward, will increase the severity of the wheel flop effect. Increasing the rotational inertia of the front wheel by increasing the speed of the vehicle and the rotational speed of the wheel will tend to counter the wheel flop effect.
A certain amount of wheel flop is generally considered to be desirable. In the magazine bike Quarterly, author Jan Heine wrote, "A bike with too little wheel flop will be sluggish in its reactions to handlebar inputs. A bike with too much wheel flop will tend to veer off its line at low and moderate speeds."
Modifications
Forks may be modified or replaced, thereby altering the geometry of the bike.
Changing fork length
Increasing the length of the fork, for example by switching from rigid to suspension, raises the front of a bike and thus decreases its head angle. Lengthening the fork would have the opposite effect on the rake of a motorcycle, since rake is measured in the opposite direction.
A rule of thumb is a 10 mm change in fork length gives a half degree change in the steering axis angle.
Changing fork offset
Increasing the offset of a fork reduces the trail, and if performed on an existing fork without lengthening the blades, shortens the fork.










