| Saab 9-3 | |
|---|---|

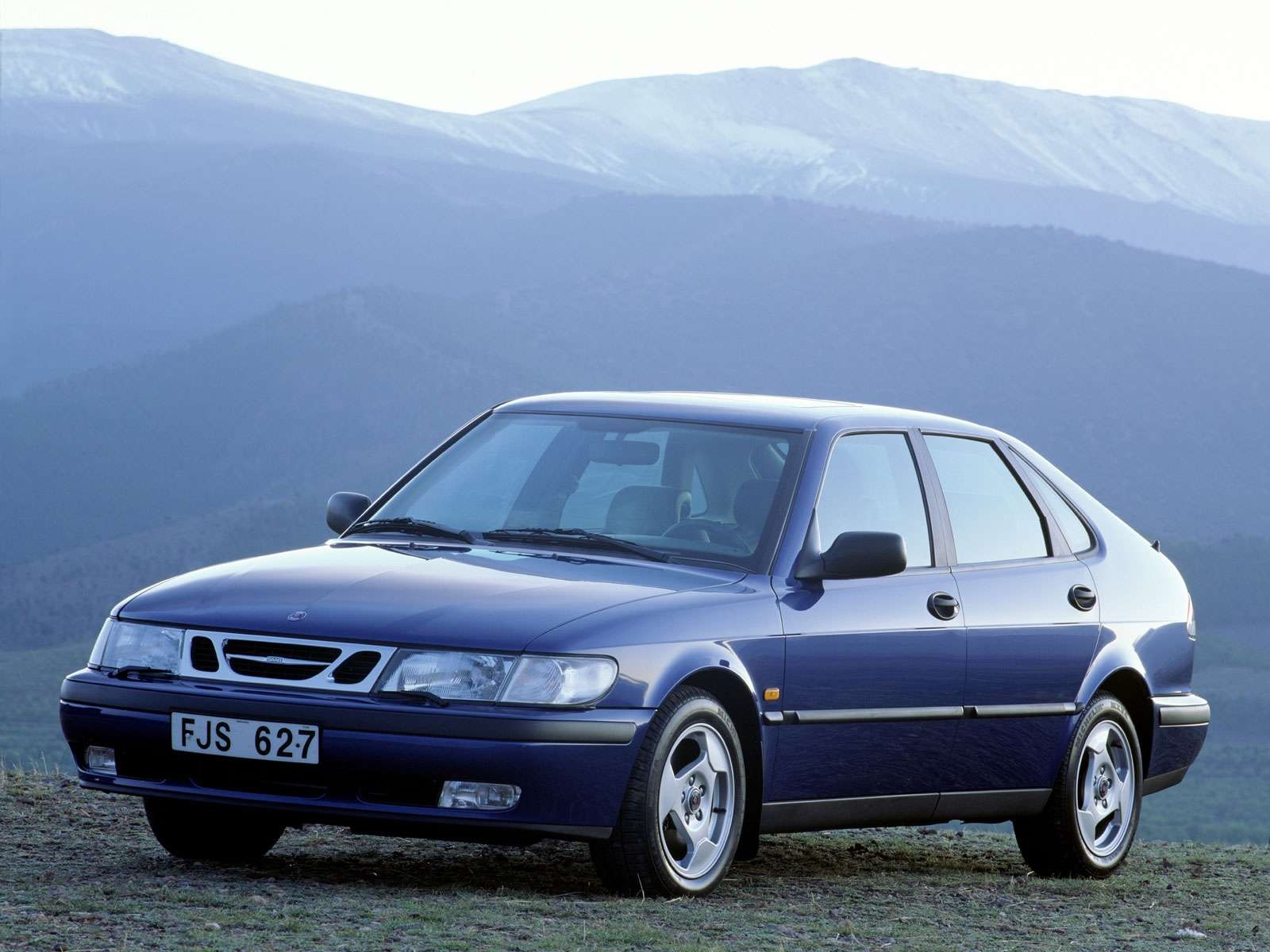
Saab 9-3 Aero Sedan MY14
|
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer |
|
| Production | 1998–2014 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Compact executive car (D) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Saab 900 |
The Saab 9-3 is a compact executive car that was originally developed and manufactured by the Swedish automaker Saab.
The 9-3 was first based on the GM2900 platform and subsequently changed to the GM Epsilon platform. Other vehicles using this platform included the Opel Vectra and Cadillac BLS. Saab's last owners, National Electric Vehicle Sweden (NEVS) were assembling the 9-3 sedan (saloon) as Saab's only model, but the company declared bankruptcy after a few hundred cars.
Overview
The car was badged as 93 starting in the 1998 model year, when Saab revised the naming strategy of their small car to match that of the larger 95. The model was advertised as 9-3, pronounced as "nine three". The Saab 9-3 was launched in 1997 for the 1998 model year essentially as a rebadged 2nd Generation Saab 900 (1994–1997 model), and succeeded by a redesigned 9-3 for the 2003 model year. It is not to be confused with the Saab 93, pronounced "ninety three", which was a car produced by Saab from 1955 to 1960.
| First generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1998–2002 |
| Assembly | Trollhättan, Sweden (hatchback) Uusikaupunki, Finland (Valmet Automotive) (1999–2003 convertible and Viggen) |
| Designer | Einar Hareide |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 3-/5-door hatchback 2-door convertible |
| Layout | Transverse front-engine, front-wheel drive |
| Platform | GM2900 platform |
| Related | Opel Vectra Saab 9-5 Saturn L-Series |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 2.0 L B204 I4 2.0 L B205 I4 2.0 L B205R I4 2.3 L B235R I4 2.2 L Turbodiesel I4 |
| Transmission | 5-speed manual 4-speed automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,605 mm (102.6 in) |
| Length | 1999–2000 Viggen & 2001–02: 4,630 mm (182.3 in) 1999–2000: 4,628 mm (182.2 in) 2001-02 Viggen: 4,640 mm (182.7 in) |
| Width | 1,712 mm (67.4 in) |
| Height | Hatchback: 1,427 mm (56.2 in) Convertible: 1,422 mm (56.0 in) 2001-02 Viggen Hatchback: 1,415 mm (55.7 in) 2001–02 Viggen Convertible: 1,410 mm (55.5 in) |




The first generation 9-3, an updated Saab 900 (NG) was launched in 1998 for the 1999 model year. It was known to enthusiasts as the OG 9-3 (old generation) and internally as body style 9400. It continued as a full line through the 2002 model year. (In 2003, Saab produced only the convertible model of this line - other models were replaced by the second generation 9-3). Saab claimed that 1,100 changes were made, including a revised suspension in an attempt to tighten up the handling characteristics of its predecessor, the Saab 900 (1994–1998 model). It featured revised styling with some models receiving a black rear spoiler and removed Saab's trademark centrally mounted "snow flap". It was available as a three or five-door hatchback, and as a two-door convertible. It was the last small Saab to use the company's H engine. Improvements over the Saab 900 (NG) also included better crash-worthiness with more extensive A-pillar reinforcements, stronger door sills and frames, standard torso/head side-airbags and Saab Active Head Restraints . The 9-3 continued the Saab safety tradition of testing the roof and A-pillar strength by simulating a collision with a moose.
The 9-3 was available with a new variant of the B204 engine (B204E, 154 hp (115 kW)), a low pressure turbo (LPT) engine based on the B204L used in the last generation Saab 900. For the U.S. market, all 9-3s received turbocharged petrol engines with the "full pressure turbo" (B204L, 185 hp (138 kW)) as the standard offering, and a "HOT" (B204R, 200 hp) variant in the SE models for the 1999 model year. The 2000 model year saw a revision from SAAB's Trionic T5.5 to Trionic 7 engine management system. The T7 based engines were the B205L with 185 hp (138 kW) and the B205R HOT engine with 205 hp (153 kW). The first generation 9-3 was also the first Saab available with a diesel engine, a unit also found in the Opel Vectra, Astra G, Signum, Zafira A. Unlike the Saab 900 (NG), the 9-3 is fitted with a CAN bus like the Saab 9-5.
A Saab innovation is the 'Night Panel', carried over from the Saab 900, which permits dousing of the instrument panel lighting, except for essential information, for less distraction when night driving.
A total of 326,370 first generation 9-3s were built.
Saab 9-3 Viggen

A high-powered version of the Saab 9-3 was the "Viggen" (English: Thunderbolt). It was named after the Saab 37 Viggen aircraft. Production ended in 2002.
It came with a turbocharged 2.3 L engine, (B235R) giving 225 bhp (168 kW; 228 PS) later 230 bhp (172 kW; 233 PS) on 1.0 bar (15 psi) of boost from its Mitsubishi TD04-HL15-5 turbocharger. Other changes included higher capacity intercooler, performance tuned ECU, flow through muffler and tip, heavy duty clutch and pressure plate, stiffened and lowered springs, firmer dampers, and stronger CV joints and driveshafts.
In 1999, the Viggen was the first 9-3 to use Saab's Trionic 7 engine management system. In addition, the 2001 model year introduced a Traction Control System (TCS) to the Viggen. TCS was later introduced to the SE line.
The car featured a special rear wing requiring relocation of the radio antenna, aerodynamically designed bumpers and side skirts, special bolstered and colored leather seats (available in four colors: black with black inserts (charcoal), black with blue inserts (deep blue), black with orange inserts (flame ochre), and tan with tan inserts), sportier suspension, bigger wheels and upgraded brakes.
The Viggen was only available with a five-speed manual transmission, CD player, power moonroof, and (what were initially) Viggen-specific motorised and heated leather seats with the Viggen delta logo embossed in the backrest; these were later also available in the Aero model (U.S. market 'SE' model) without the embossed Viggen logo. Some colors featured carbon-fibre interior trim from its introduction to the middle of the 2001 model year, when Saab substituted a less expensive printed gray pattern for the dash and standard trim.
New Viggen buyers in the U.S. were offered two days of advanced driving instruction at Road Atlanta and dined with Saab USA executives from nearby Norcross, Georgia.
Some motoring journalists were critical of untamed torque steer in low gears.
Production summary
| Viggen Production Summary | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Models produced | Models imported into the U.S. | ||||
| Model Year | Yearly total | Total | Convertible | 3-door | 5-door |
| 1998 | 14 | ||||
| 1999 | 1,099 | 426 | 426 | ||
| 2000 | 1,621 | 804 | 245 | 138 | 421 |
| 2001 | 1,251 | 1,152 | 738 | 129 | 285 |
| 2002 | 615 | 550 | 322 | 71 | 157 |
| Total | 4,600 | 2,932 | 1,305 | 764 | 863 |
4,600 Viggens were manufactured until production ended in June, 2002; of which 500 units were produced for the UK market. For 1999, 426 3-door Viggens were imported into the U.S.; of those 420 were blue, 2 were silver, 2 were Monte Carlo yellow, and 2 were black.
First generation 9-3 engines

Other than the diesel engines, all the first generation engines were versions of the Saab H engine. Other than the Saab 9-5, the first generation 9-3 was the last to utilise this all Saab engine design. All versions of this engine feature a DOHC 16-valve design with Saab's Saab Direct Ignition. All turbocharged engines utilise Saab's Trionic engine management system which works hand in hand with the Direct Ignition's IDM module (mounted to the top of the engine, directly engaging the sparkplugs). The later two technologies were migrated into other GM products during the ten years that GM controlled Saab. All of the engines, other than the normally aspirated version and the low-pressure turbo, had high specific power outputs. The B205R generated 102.5 horsepower (76.4 kW) per litre and 252 lb·ft (342 N·m) of torque.
| Engine | Displacement | Torque | Power | Compression ratio | Boost pressure | Model Years Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B204i: | 2.0L (1985cc) | 177 N·m (131 lb·ft) @ 4300 rpm | 130 hp (97 kW) @ 5500 rpm | 10.1:1 | - | 1999-2000 |
| B204E: | 2.0L (1985cc) | 219 N·m (162 lb·ft) @ 3600 rpm | 154 hp (115 kW) @ 5500 rpm | 9.2:1 | 0.40 bar (5.8 psi) | 1999-2000 |
| B204L: | 2.0L (1985cc) | 263 N·m (194 lb·ft) @ 2100 rpm | 185 hp (138 kW) @ 5500 rpm | 9.2:1 | 0.73 bar (10.6 psi) | 1999 |
| B204R: | 2.0L (1985cc) | 280 N·m (210 lb·ft) @ 2200 rpm | 200 hp (150 kW) @ 5500 rpm | 9.2:1 | 1.00 bar (14.5 psi) | 1999 |
| B235R: | 2.3L (2290cc) | 342 N·m (252 lb·ft) @ 1950 rpm | 225 hp (168 kW) @ 5500 rpm | 9.25:1 | 1.08 bar (15.7 psi) | 1999–2002 |
| B205E: | 2.0L (1985cc) | 240 N·m (180 lb·ft) @ 1800 rpm | 150 hp (110 kW) @ 5500 rpm | 9.2:1 | 0.40 bar (5.8 psi) | 2000–2002/3 |
| B205L: | 2.0L (1985cc) | 280 N·m (210 lb·ft) @ 1800 rpm | 185 hp (138 kW) @ 5500 rpm | 9.2:1 | 1.00 bar (14.5 psi) | 2000–2002/3 |
| B205R: | 2.0L (1985cc) | 280 N·m (210 lb·ft) @ 1800 rpm | 205 hp (153 kW) @ 5500 rpm | 9.2:1 | 1.00 bar (14.5 psi) | 2000–2002/3 |
| 2.2TiD: | 2.2L (2171cc) | 260 N·m (190 lb·ft) @ 1800 rpm | 116 hp (87 kW) | 19.5:1 | 0.90 bar (13.1 psi) | 1998 – Sept. 2000 |
| 2.2TiD: | 2.2L (2171cc) | 285 N·m (210 lb·ft) @ 1750 rpm | 125 hp (93 kW) | 18.5:1 | 0.90 bar (13.1 psi) | Sept. 2000 – Aug. 2002 |